Operational Technology Security Posture Management (OTSPM) is the process of continuously monitoring industrial environments for security threats and mitigating them.
Point solutions for Operational Technology (OT) focus on specific areas of an industrial deployment lifecycle. In contrast, OTSPM solutions focus on all of them and correlate data between areas. As a result, they can detect more threats and speed up day-to-day operations.
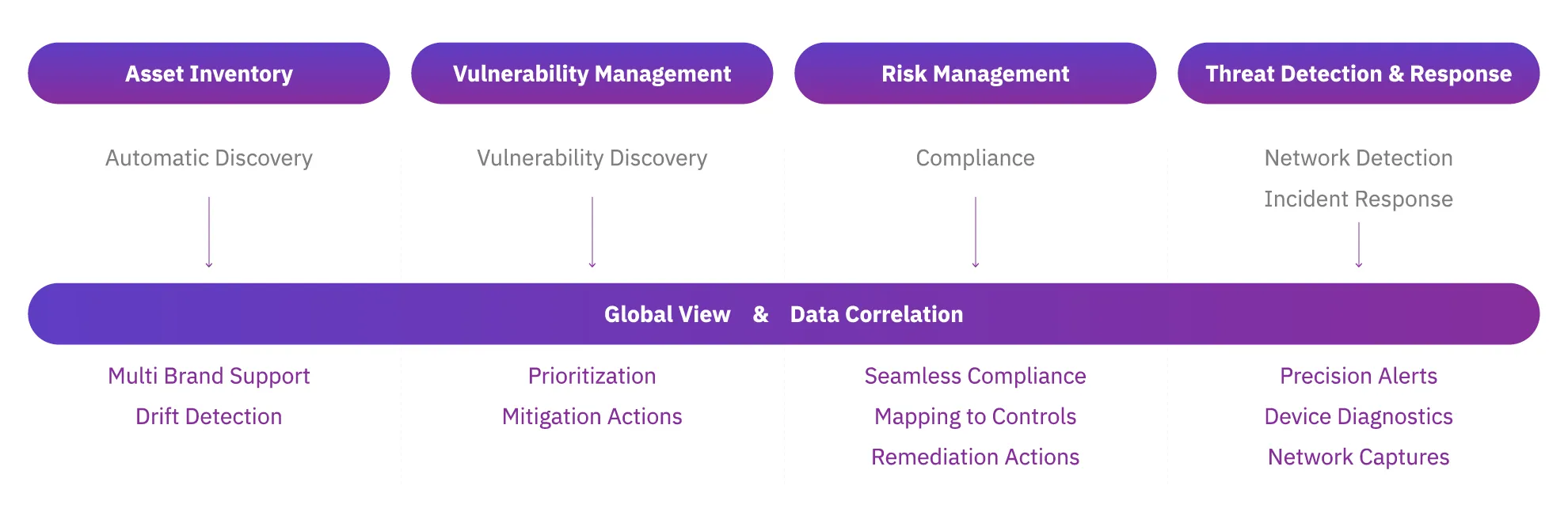
Here is a list of the key areas in OT security and how OTSPM expands each of them:
Asset Inventory: Automatically discover the devices on the network and gather relevant context to inform the rest of decisions.
- With OTSPM: By correlating inventory with network detection, you can update your inventory in real time as activity from new devices is detected. You can also keep a changelog of the inventory tracking, for example, when the properties of a PLC change.
Vulnerability Management: Correlate your inventory against vulnerability databases and best practices to measure your attack surface.
- With OTSPM: Use context to calculate the real impact of each vulnerability in your infrastructure, helping you prioritize the most critical ones. Also, tailor mitigation actions to reduce your attack surface.
Risk Management: Check if you meet security standards and benchmark requirements.
- With OTSPM: Run compliance checks continuously to identify when devices fall out of compliance and apply remediation actions.
Threat Detection and Response: Detect abnormal behaviors that could indicate ongoing attacks. Gather relevant context to stop them and prevent them from happening again.
- With OTSPM: Include your infrastructure context in the rules evaluation to avoid false positives and reduce noise. Check the devices’ diagnostics to detect misconfigurations, such as devices using default credentials.
Global View (with OTSPM): Check the security posture for all your facilities at a glance on a single pane of glass. This makes you more efficient and provides a big picture that can highlight global trends.
How does OTSPM Differ From IT Security?
Industrial deployments share a lot in common with a regular IT installation, it’s all computers and networks after all. However, a few radical differences make OT so different that traditional IT security tools fall short inside an industrial environment, thus, needing a new paradigm and toolbox.
OT is Mission-Critical
Stopping a production line is expensive, and it’s not feasible to have empty production lines lying around to ensure high availability. OT security tools must be especially precise when alerting, taking special care to avoid false positives that stop production.
OT has a Physical Plane
An industrial facility can host hundreds of devices spread across the plant. OT security tools must support security engineers on the field, helping them find the devices that need checking.
Device Management in OT is Different
There are three main ways OT devices are managed differently than IT equipment:
- Security updates are applied using an external computer and must be carefully planned to avoid impacting production.
- You must track changes on the PLCs (industrial computers) software to detect some attacks.
- Commonly, manufacturers perform remote maintenance on OT equipment. These accesses need to be accounted for and secured.
OT has its Relevant Context
PLCs and other industrial equipment are too simple to install security probes. Security tools need to speak the language of these devices across multiple brands to retrieve diagnostic data relevant to security.
OT has Specific Compliance Requirements
The most common security standards and benchmarks for IT also apply to OT. By using OTSPM tools, you’ll automate the bulk of your audits, as opposed to security tools that don’t integrate well with OT equipment, which results in many manual checks.
In addition to general standards, the industry has its security regulations and standards, like Purdue or TISAX. Using generic security tools will make it harder to meet industry-specific requirements.
If you want to learn more about the differences between OT and IT, check out: Five Reasons Why IT Security Tools Fall Short To Secure the Industry
How Does OTSPM Differ from CSPM?
OTSPM and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) differ in the type of assets they want to secure and their strategies for achieving this. OTSPM focuses on industrial equipment and physical infrastructures, while CSPM focuses on cloud services and access control.
In both processes, you’ll find the same areas: Inventory, Vulnerability Management, Risk Management, and Threat Detection. You’ll also find the approach of correlating data across areas to detect more threats.
However, industrial assets are so different from cloud assets that the tools and strategies of OTSPM and CSPM completely differ.
OTSPM has Metal, CSPM has Services
OT security engineers have to manage and secure physical hardware. This includes managing firmware versions, creating VLANs to isolate areas, and managing physical access to the devices.
On the other hand, cloud engineers manage services that run inside the cloud provider’s infrastructure. They don’t have to worry about the system their services run on; however, they need to manage the roles and permissions on the accounts that access the cloud.
When monitoring the infrastructure, an OTSPM tool relies heavily on an on-premises agent that scans the network traffic and gathers device diagnostic information. Conversely, a CSPM tool will use a mixture of agents installed on the assets and agentless solutions that read the cloud logs through the cloud provider API.
Asset Inventory
In an industrial deployment, an OTSPM tool will gather the asset inventory by scanning the network for connected devices.
A CSPM tool will have an easier job, as it only needs to query the cloud provider’s API to gather a list of services.
Vulnerability Management
OTSPM searches for vulnerabilities in the device’s firmware. Devices are usually so simple that there aren’t operating systems or libraries to worry about.
Cloud environments are more heterogeneous, including services based on virtual machines, containers, or code alone. A CSPM tool will be able to identify operating systems, base images, and libraries to provide a comprehensive list of vulnerabilities.
Risk Management
General security standards like NIST or NIS2 apply to both cloud and industrial environments.
Cloud environments tend to gather more personal data, so CSPM tools focus more on standards like PCI or GDPR.
The industry has specific regulations, so OTSPM tools focus more on standards like Purdue or TISAX.
Threat Detection and Response
Some abnormal behaviors may indicate a compromise in both the Industry and the cloud, such as Access to suspicious addresses, broadcast traffic, or new and unexpected resources.
Beyond network traffic and inventory, OTSPM tools will also track changes in device configuration, as many attacks tend to affect production by changing the program’s parameters.
CSPM tool will heavily monitor the activity of cloud accounts, detecting people logging in without multi-factor authentication, connecting from a different location from where they reside, or accessing resources they shouldn’t. All these are indicators of a compromised account.
What Should Organizations Look for When Choosing an OTSPM Solution?
When considering an OTSPM solution, you should look for a tool that integrates well with your infrastructure, detects the most important threats, and guides you in strengthening its security.
Let’s apply these guidelines to more specific areas.
Go Beyond Checking Boxes
Some tasks like compliance are often considered a burden. As such, most security tools only cover the basics.
Look for tools that go beyond automating chores and turn them into a guide that helps you improve security. For example, turn compliance into a continuous check that can warn when drift occurs, and your assets fall out of compliance. Then, it provides steps to help you remediate the situation.
Legacy and Multi-Brand Support
Some security vendors will only work with one brand or won’t support legacy equipment that works fine.
Choose tools with multi-brand support that will allow you to include a wide range of devices in your infrastructure.
Wide Visibility and Precision
Look for the blind spots in the security solutions you are considering, and make sure that your OTSPM tool covers the most critical areas.
But being able to see everything is worthless if you are bombarded with non-critical insights.
Look for tools that cut through the noise and help you prioritize with their insights and alerts.
Adaptability to Your Needs
Necessities change and evolve. Tools often are too opinionated to make things for you, but this can be a limiting factor if they don’t offer customization.
Look for tools that allow you to adapt them to your needs, such as those with customizable reporting, rules, or compliance controls.
Integration With 3rd Party Tools
On the same note, stay open to possibilities by choosing tools that allow you to expand their functionality by integrating with other tools.
What Future Trends Could Impact OTSPM?
The industry is adapting technology at a blazing speed. We are observing the following trends catching up.
The Rise of IoT
More and more devices, including sensors, item trackers, and transportation robots (AMRs), are connected inside industrial plants.
Companies need to start preparing to manage and secure all these new devices.
Merging of OT, IT, and Cloud
As the digitalization of the industry advances, the industrial side becomes more integrated with the rest of the business. For example, traditionally industrial-centric companies are developing websites and mobile apps to add value to their businesses.
The teams that used to secure industrial equipment are now expanding their responsibilities.
As a result, we foresee that security tools will expand in scope, blurring the lines between OT, IT, and the Cloud.
AI Will be the Future, Eventually
The rise of generative AI has shocked the world. Although this technology is in its infancy and has more gaps than companies would like to admit, other types of AI have been proven reliable and are being used in production environments.
AI adoption will continue to grow, although it isn’t clear how and when.
We know AI is rather good at detecting outlying data in statistical sets, so we can expect that one of its first uses in security will be identifying anomalies in the network or production parameters.
Two big challenges are blocking the adoption of AI in security tools:
- AI still provides too many false positives, which wastes security engineers’ time.
- AIs are designed as black boxes, often not providing enough context to investigate security insights.
Key Ideas
OTSPM is a holistic view of industrial security, where information from several areas is correlated to detect more threats.
OTSPM shares the same spirit of IT security and CSPM but doesn’t use the same tools and strategies due to their differences.
When choosing an OTSPM tool, ensure it integrates well with your infrastructure, detects the most important threats, and guides you in strengthening its security.